A Spigelian hernia forms through the Spigelian aponeurosis. This is a layer of muscular strength that rests between the sidelong edge of the rectus muscle and the linea semilunaris.
An untreated Spigelian hernia can cause inconveniences. This makes it critical to get fast clinical treatment.
Table of Contents
What Does a Spigelian Hernia Feel Like?
If you feel a slight bump or lump on your stomach divider, you might have a Spigelian hernia. Usually covered by fat, this irregularity or lump is usually visible and more observable when you are standing. The actual size, however, often increases and decreases all by itself.
Having this kind of hernia could likewise cause:
- Torment in your midsection, not connected with food or sickness
- The torment that intensifies while stressing to hack, for instance, while trying to pass something or lifting something weighty
- An adjustment of your gut propensities, similar to obstruction
- Blood in your stools
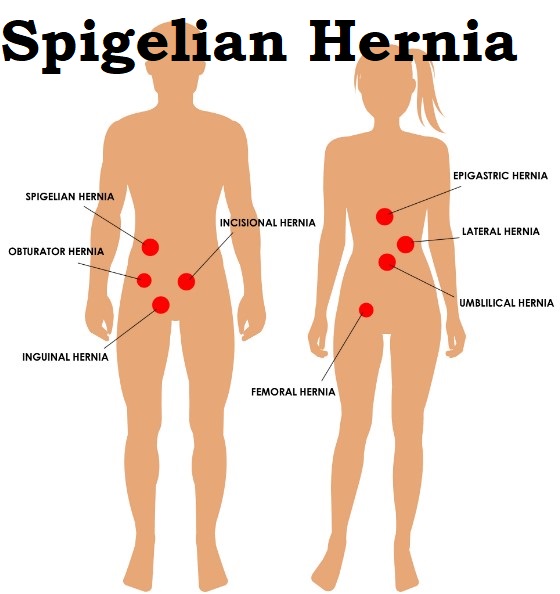
What is a Fat-Containing Spigelian Hernia?
Spigelian hernia is the distension of preperitoneal fat, peritoneal sac, or organ(s) through an intrinsic or obtained imperfection in the Spigelian aponeurosis, which situates in the aponeurotic layer between the rectus abdominis muscle medially, and the semilunar line horizontally.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing a Spigelian hernia can be troublesome, so announcing side effects to your doctor is critical. An ultrasound or CT examination of the mid-region can assist with a determination.
It might be helpful to consult a general specialist, as these experts have broad information on hernias, including it.
It may likewise find during a medical procedure or methodology performed for different reasons, including:
- a gut impediment or blockage
- exploratory medical procedure
- medical procedure for a new type of hernia
- gynecological medical procedure
- colonoscopy for colon malignant growth screening
- To analyze it, a specialist will take a complete clinical history and will conduct tests to rule out other clinical issues.
- An ultrasound can detect most cases. Specialists sometimes also use computed tomography or CT scanning. Both are painless and safe demonstration tests that permit a specialist to visualize muscles, digestive tracts, and stomach divider.
- In any case, if the determination isn’t clear, a specialist might think that a hernia is available without realizing which type. They might choose to undergo an exploratory medical procedure to find and fix the hernia.
Causes
Spigelian hernias result in a debilitated region in the stomach divider muscles.
The debilitated region can be something an individual has, or it can be acquired over the long haul. If it persists for a long time, it is usually the result of a physical issue or an increased strain inside the stomach pit. This debilitated region permits tissue and organs to penetrate through the Spigelian belt.
Risk factors include:
- a constant hack, for example, with the lung condition COPD
- much of the time stressing to have a solid discharge
- injury to the midsection, for example, during a medical procedure or because of a significant physical issue
- regularly stressing to lift weighty articles
- the liquid in the midsection because of conditions like liver issues
- being overweight
- being pregnant
Treatment for a Spigelian Hernia
Spigelian hernias treat by a medical procedure known as a hernia fix. The choice to have a medical procedure depends on the size of the hernia and whether you experience any pain. Assuming you decide on a medical procedure, a specialist can perform an open cross-section fix by making an entry point in your midsection close to the hernia. The specialist moves protruding tissue and organs back to the appropriate area, and then seals the opening in your stomach divider.
It is also possible to treat the hernia by using a minimally invasive method called laparoscopic hernia fixation. A specialist makes a more modest entry point in your midsection and fixes the hernia utilizing a slim careful instrument with a camera integrated as far as possible.
Risks and Recuperation
Medical procedures such as these can be done on a short-term basis, or you can stay one night at the clinic. Recuperation can take between three to about a month and a half with an open cross-section fix, and one to about fourteen days with a laparoscopic hernia fix. You should avoid strenuous activity during recuperation.
Chances related to a medical procedure include draining or swelling under the skin and diseases. See a specialist immediately if you experience prolonged pain, a fever, or heaving after a hernia repair procedure.
FAQs
The hernia can be diagnosed with a CT or ultrasound, but these can be erroneously negative, so the unequivocal radiological finding preceding a medical procedure is interesting.
These are uncommon stomach divider absconds that happen at the semilunar line parallel to the rectus abdominis muscle. Most patients present with indicative detainment of preperitoneal fat or intra-stomach viscera. Radiographic investigations are also helpful in confirming the conclusion.
The Spigelian hernia is an unusual condition that develops after the age of 50 mainly in men. There are usually several reasons for this, including debilitating of the stomach divider, injury, or delayed actual pressure. These are tested now and then to analyze or distinguish them from other stomach issues.
A Spigelian hernia results from a cut-like deformity in the foremost stomach divider contiguous to the semilunar line. Moreover, the vast majority of these happen in the lower midsection where the back sheath is insufficient. The hernia ring is a clear-cut imperfection in the crosses over aponeurosis.
Conclusion
It can be tempting to delay looking for treatment for unexpected stomach discomfort. This response might be particularly evident if the torment disappears for some time. In any case, it presents serious clinical risks.
They are generally simple to treat, and a great many people won’t require a medical procedure once more. Along these lines, when indications of a Spigelian hernia show up, individuals ought to see a specialist.
